Construction.jpg) | (RABH) Construction
|
| The Reverse Air Bag House (RABH) is a custom - built filter designed for cleaning gases with typically high flow rates and high temperatures.
The typical RABH is in modular construction with four or more independent modules. The extra space created between the hoppers provides a large passage way between rows down the middle of the
system. This passage way is divided into three sections horizontally to make the inletplenum,outletplenum, and the reverse-air plenum. This construction not only offers control on the velocity profiles, but
also facilitates on-line maintenance. Each module can be isolated for inspection or maintenance by closing inlet, outlet and reverse air dampers, while other modules are still in operation. The units, being
custom built and voluminous, are dispatched knocked down to structures and panels.
|
|
NormalGasFlow.jpg) | (RABH) Normal Gas Flow
|
| The dust laden gas to be cleaned enters the common inlet plenum. A portion passes through each inlet damper into
the hopper area below each module. The dust laden gas then passes through the tubesheet to the inside of each bag. Virtually all the gas - borne dust particles are separated, to meet the outlete mission levels required, as the gas passes through the bags. Clean gas enters the outlet plenum through the open outlet damper.
|
|
 | (RABH) Reverse Gas Flow
|
| Each module is periodically and automatically shut-down for a brief reverse-air cleaning cycle, as per the system logic built in, with the help of the automatic sequential controllers; the latter controls various cycles like the interval time, close time, reverse - air time and the settle time. Clean gas is drawn from the outlet plenum by the reverse - air fan into the reverse -air plenum during cleaning. During this process, the outlet damper is closed and the reverse - air damper is opened letting in the reverse air in a direction opposite to the normal dusty gas flows. This action slowly collapses the bags, breaking up the dust cake on the inner surfaces of the bags, there by allowing the dust to get discharged to the hoppers.
|
|
 |
| Bag Diameter(mm) |
| 125 |
203 |
292 |
| 4200 |
7000 |
10370 |
|
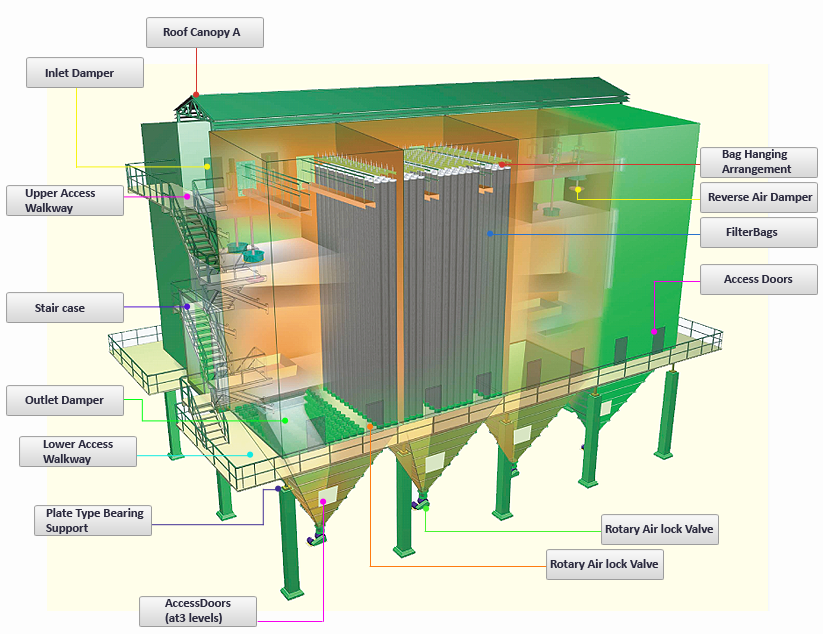
 | Poppet Damper
|
| The poppet outlet and reverse air dampers operate vertically, thus ensuring optimum sealing. These are sized appropriately for the application, in order to keep inlet, outlet & reverse air velocities low. This reduces both wear and pressure drop.
|
|
 | Inlet Damper
|
| Each module is provided with inlet manual damper to suit the inlet nozzle of the hopper. These are without - board bearings to avoid abrasion and erosion as they are not exposed to dust laden gases.
|
|
 | PTFE Expansion
|
| Bearing support separates hot & cold zones of the equipment. Thermal expansions of the equipment are taken care by these bearings with out developing stress in structures.
|
|
 | Tensioning Tool
|
| Supplied a standard accessory, this ensures bag fit mentin minutes and extends bag life by applying appropriate tension accurately and consistently.
|
|
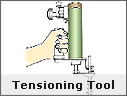
 | Bag Hanging Arrangement
|
+ J-Hook with conical spring - normally the standard option.
+ J-Hook with pin arrangement - typically preferred option for carbon black applications.
|
|
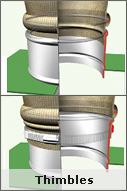 | Thimbles
|
Thimbles facilitate uniform distribution of gas flow into the bags without impact on bags. The construction is such that bags will never slip - out as they are located using clamp or snap band arrangement. To ensure the positioning of the thimble and bag, in terms of verticality, the assembly is normally carried out at site.
+Snap band Type and +Clamp-onType
|
|
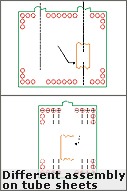 | Different tubesheets
|
| Different assembly arrangements on tube sheets
|
|
Different Bag lengths & diameters |
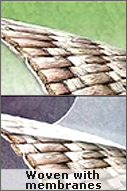 | Woven with Membranes
|
Different Bag types
+ Woven and + Woven with membranes
|
|
Applications |
   
|